How We Fight Fire
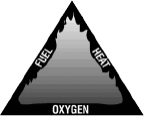
Wildland fires are suppressed by upsetting the combustion process by removing one of the legs of the fire triangle.

The fuel leg is removed by creating a fireline around the fire where vegetation is removed down to mineral soil. This is the most common method utilized by firefighters and can is accomplished by mechanized equipment (dozers) or hand crews.
TDF dozer building a direct (immediately adjacent to the fires edge) fireline through heavy fuels
A black line is where the fireline is immediately adjacent to the burned edge of the fire. This is the desired condition of a completed fireline. A black line provides a safe area for firefighters to take refuge if necessary and aids in control of the fire.
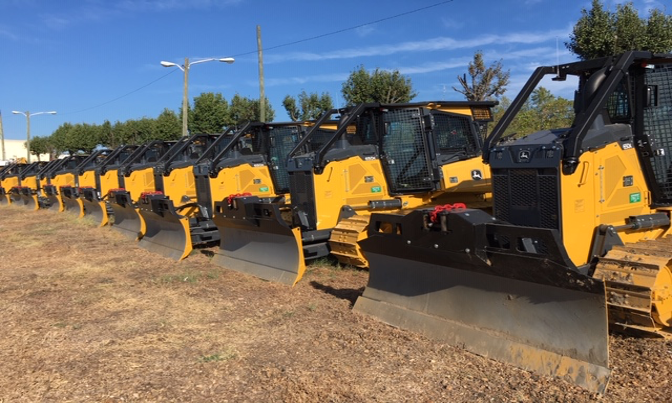

To meet the challenge of suppressing unplanned ignitions the division staffs 112 type 3 dozers and 94 type 6 engines across the state. During the peak of fire season, some counties staff 5 person crews to assist with suppression response requirements.
The current fleet is made up of Caterpillar D-3 and D-4 dozers. Most of these dozers are over twenty years old and are being phased out for new John Deere 650’s (pictured above).
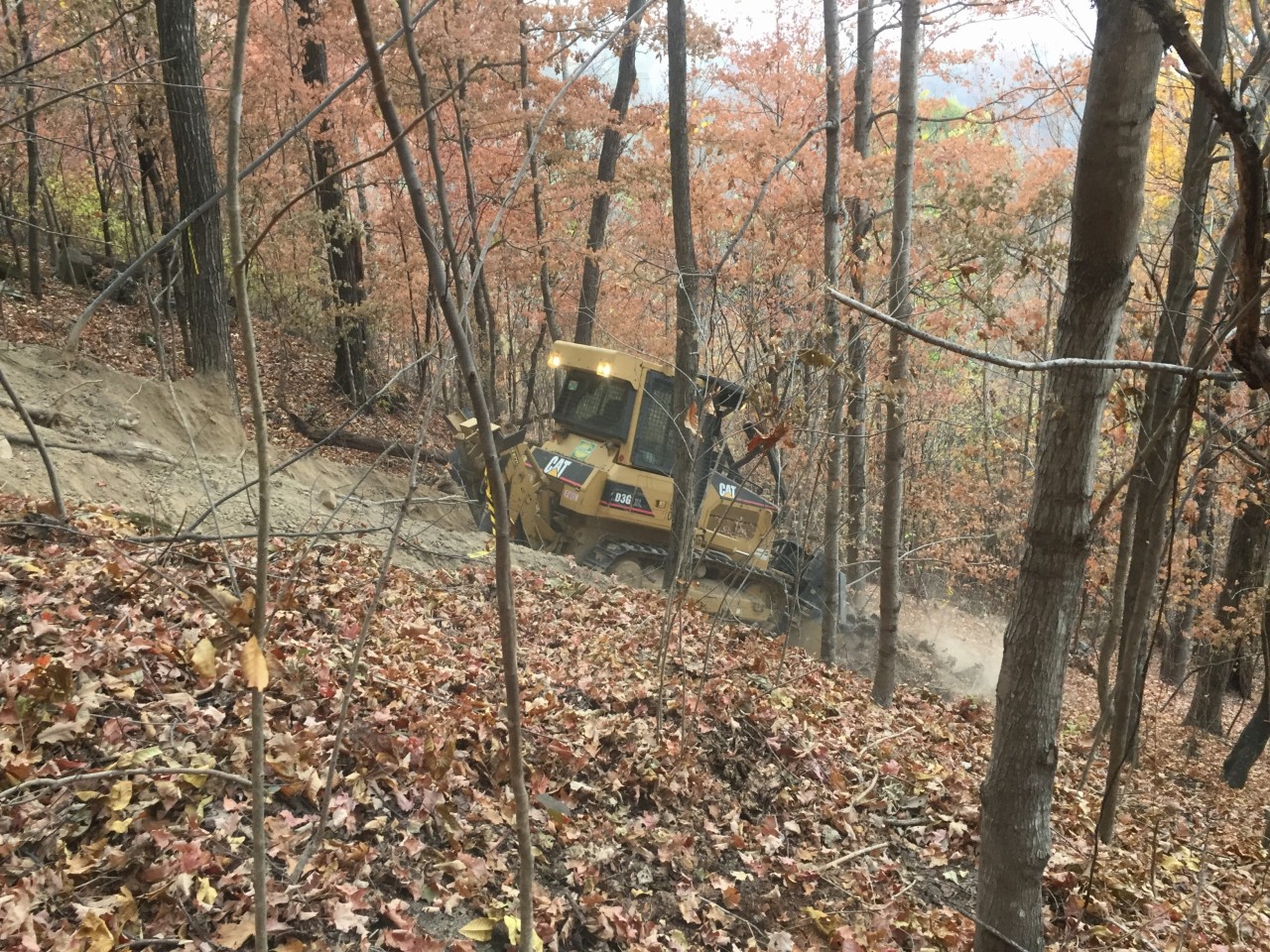

In rough steep terrain or where the fire is very intense, indirect line (located away from the fires edge that is suitable for working) is often constructed.

TDF hand crew constructing fireline with hand tools. Flammable ground fuels are scraped away to bare mineral soil to deprive the fire of fuel. Hand crews are used in terrain that is inaccessible for dozers.
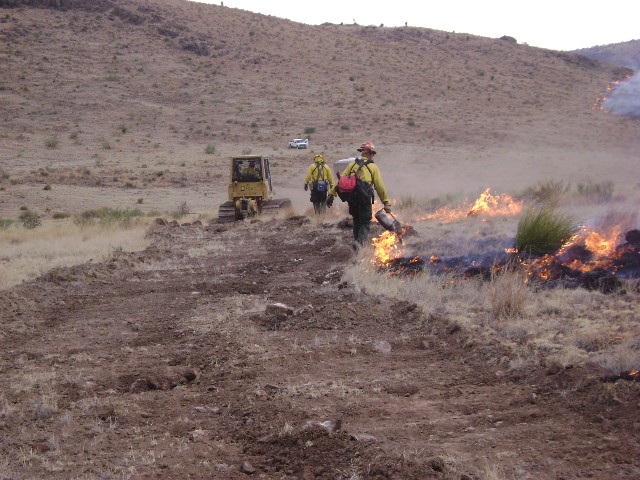

Often hand crews will work in conjunction with dozers while building fireline. Here firefighters using drip torch toBurn-out pockets of fuels behind the dozer which creates a black line.
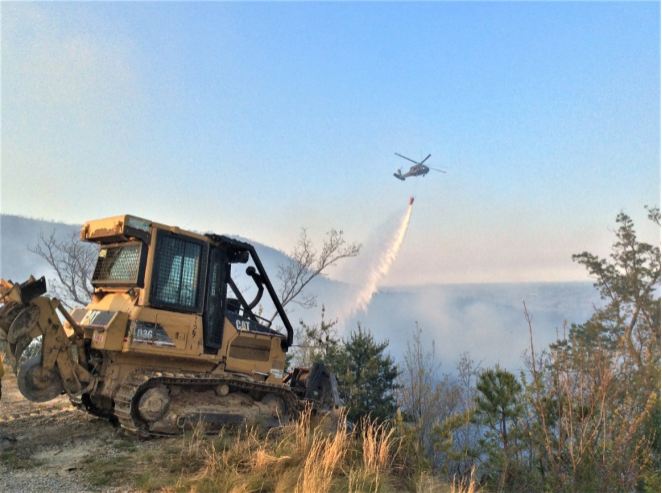

Fire fighting aircraft are often called into assist when fires are burning very intensely with rapid rates of spread. Aircraft dropping water or retardant can aid in slowing the spread of a wildfire so that ground resources can contain it. The Division of Forestry is partners with the TN Army National Guard who provides Black Hawk Helicopters for firefighting missions.
Federal Contract Airtankers are available to the TDF. Airtankers can be activated by an order to the multi-agency Coordination Center in Atlanta, Georgia.
Prompt clear communications are essential for effective and safe operations. Communication is the basis of our risk management process and explicitly listed in several fire orders and watch-out situations. The division communicates using base unit and mobile radios linked by repeaters statewide. The division of Forestry dispatches emergency resources in four zones across the state; each zone headquarters is located in a district office. The Fire Resource Coordinator for each district t is responsible for dispatching and tracking resources. The Nashville office provides overall state coordination. The Division and its federal partners operate on the Very High Frequency (VHF) band width. The mobile handheld radios are currently being upgraded to Bendix/King programmable radios.
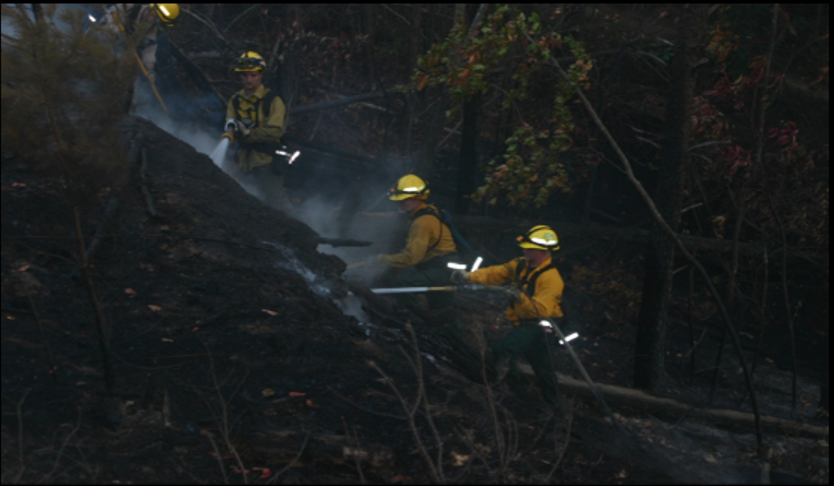

The heat leg is upset by applying water or water/foam mixture by engines. Soil thrown by firefighters can also cool fuels below the combustion temperature.Firefighters applying water to burning fuels.
Soil that is thrown with shovels and fire flappers can be used to smother lower intensity fires thereby starving a fire of oxygen. Some common tools used in fire suppression include shovel, council rake, Pulaski, Fire Swatter or flapper, chain saw, backpack blower. Ignition devices are also used which would include the fusee and drip torch, flare launcher.